How to Mix BPC-157 Safely
Guide
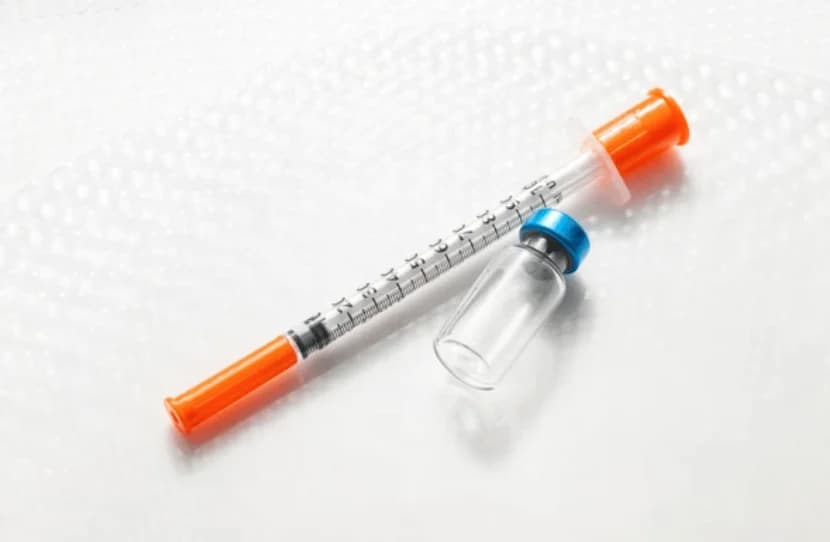
BPC-157 is a research peptide studied for its potential effects on tissue repair and inflammation. Accurate mixing with bacteriostatic water ensures consistent concentrations that align with your protocol and reduces unnecessary waste.
What You'll Need
- Lyophilized BPC-157 vial (commonly 2 mg or 5 mg)
- Sterile bacteriostatic water
- 1 mL insulin syringe with 29–31G needle
- Alcohol prep pads and sterile work surface
- Sterile mixing needle (18–22G) if available
- Peptide storage containers or aliquot vials
Step-by-Step Mixing Instructions
- Sanitize the workspace: Wipe your surface with 70% isopropyl alcohol and wash your hands thoroughly. Follow sterile compounding practices outlined in USP <797>.2
- Reconstitute slowly: Draw the required volume of bacteriostatic water into your syringe, insert the needle through the vial stopper, and allow the water to run down the inside wall to minimize foaming.
- Gently dissolve: Swirl the vial in small circles. Avoid shaking, which can denature the peptide.1
- Label the vial: Record concentration, date mixed, and storage instructions before refrigerating at 2–8°C.
Calculate Your Target Concentration
Once BPC-157 is dissolved, determine the concentration and draw volume needed for each dose. The Peptide Calculator instantly converts mg to mL, accounts for custom vial strengths, and maps the required units on standard insulin syringes.
Example Mix
For a 5 mg vial mixed with 2 mL bacteriostatic water, the solution concentration is 2.5 mg/mL. A 250 mcg dose equals 0.1 mL (10 insulin units). Use the calculator to adjust for alternate strengths or multi-dose regimens.
Best Practices for Storage and Stability
- Refrigerate reconstituted BPC-157 at 2–8°C and protect from light.1
- Use sterile, single-use insulin syringes to avoid cross-contamination.
- Create small aliquots to minimize repeated vial punctures.3
- Discard any solution showing discoloration or particulate matter.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Foaming or bubbles: Inject solvent along the vial wall and allow the solution to settle before drawing doses.
- Incomplete dissolution: Warm the vial between gloved palms and swirl gently; avoid heat sources.
- Incorrect dose volume: Recalculate using the Peptide Calculator to confirm concentration and syringe draw.
References
- Šikić et al., 2020: Šikić, P. et al. "Stable Gastric Pentadecapeptide BPC 157: Discovery, Achievements, and Future Perspectives." Current Pharmaceutical Design 26, no. 3 (2020): 309-325. Source
- USP <797>, 2023: United States Pharmacopeia. USP <797> Pharmaceutical Compounding - Sterile Preparations. United States Pharmacopeial Convention, 2023. Source
- WHO, 2010: World Health Organization. "WHO Good Practices for Pharmaceutical Compounding of Medicinal Products for Human Use." Annex 7, Technical Report Series 961, 2010. Source